对于较多数量的文件描述符的监听无论是select还是poll系统调用都显得捉襟见肘,正如前文Unix/Linux 中的五种 I/O 模型中对select/poll与epoll性能对比中所分析的,poll每次都需要将所有的文件描述符复制到内核,内核本身不会对这些文件描述符加以保存,这样的设计就导致了poll的效率的低下。而epoll则对此做了相应的改进,不是epoll_wait的时候才传入fd,而是通过epoll_ctl把所有fd传入内核,再一起”wait”,这就省掉了不必要的重复拷贝。其次,在 epoll_wait时,也不是把current轮流的加入fd对应的设备等待队列,而是在设备等待队列醒来时调用一个回调函数(当然,这就需要“唤醒回调”机制),把产生事件的fd归入一个链表,然后返回这个链表上的fd。另外,epoll机制实现了自己特有的文件系统eventpoll filesystem。本文将从linux内核源码(linux v2.6.26.8)角度出发对epoll的实现机制加以总结梳理。
epoll初始化
当系统启动时,epoll会进行初始化操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
static int __init eventpoll_init(void)
{
mutex_init(&epmutex);
/* Initialize the structure used to perform safe poll wait head wake ups */
ep_poll_safewake_init(&psw);
/* Allocates slab cache used to allocate "struct epitem" items */
epi_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_epi", sizeof(struct epitem),
0, SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN|EPI_SLAB_DEBUG|SLAB_PANIC,
NULL);
/* Allocates slab cache used to allocate "struct eppoll_entry" */
pwq_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_pwq",
sizeof(struct eppoll_entry), 0,
EPI_SLAB_DEBUG|SLAB_PANIC, NULL);
return 0;
}
fs_initcall(eventpoll_init); |
上面的代码实现一些数据结构的初始化,通过fs/eventpoll.c中的注释可以看出,有三种类型的锁机制使用场景:
1.epmutex(mutex):用户关闭文件描述符,但是没有调用EPOLL_CTL_DEL
2.ep->mtx(mutex):用户态与内核态的转换可能会睡眠
3.ep->lock(spinlock):内核态与具体设备中断过程中的转换,poll回调
接下来就是使用slab分配器动态分配内存,第一个结构为当系统中添加一个fd时,就创建一epitem结构体,内核管理的基本数据结构。
内核数据结构
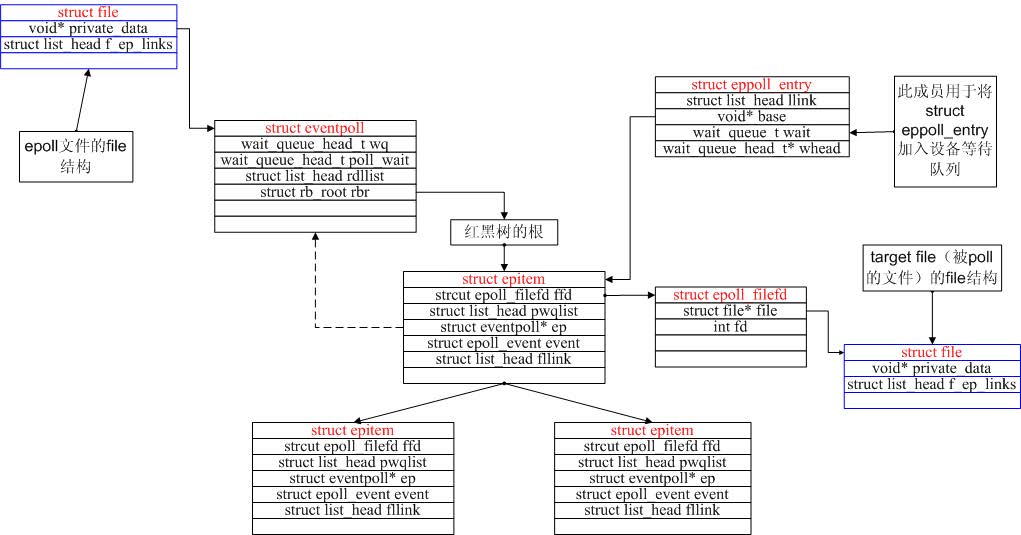
前文我们已经知道epoll在内核主要维护了两个数据结构eventpoll与epitem,其中eventpoll表示每个epoll实例本身,epitem表示的是每一个IO所对应的的事件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
struct epitem {
/* RB tree node used to link this structure to the eventpoll RB tree */
struct rb_node rbn; /*用于挂载到eventpoll管理的红黑树*/
/* List header used to link this structure to the eventpoll ready list */
struct list_head rdllink; /*挂载到eventpoll.rdlist的事件就绪队列*/
/*
* Works together "struct eventpoll"->ovflist in keeping the
* single linked chain of items.
*/
struct epitem *next; /*用于主结构体中的链表*/
/* The file descriptor information this item refers to */
struct epoll_filefd ffd; /*该结构体对应的被监听的文件描述符信息(fd+file, 作为红黑树的key)*/
/* Number of active wait queue attached to poll operations */
int nwait; /*poll(轮询操作)的事件个数
/* List containing poll wait queues */
struct list_head pwqlist; /*双向链表,保存被监视文件的等待队列,功能类似于select/poll中的poll_table;同一个文件上可能会监视多种事件,这些事件可能从属于不同的wait_queue中,所以需要使用链表
/* The "container" of this item */
struct eventpoll *ep; /*当前epitem的所有者(多个epitem从属于一个eventpoll)*/
/* List header used to link this item to the "struct file" items list */
struct list_head fllink; /*双向链表,用来链接被监视的文件描述符对应的struct file。因为file里有f_ep_link用来保存所有监视这个文件的epoll节点
/* The structure that describe the interested events and the source fd */
struct epoll_event event; /*注册感兴趣的事件,也就是用户空间的epoll_event
};
|
而每个epoll fd对应的主要数据结构为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
struct eventpoll {
/* Protect the this structure access */
spinlock_t lock; /*自旋锁,在kernel内部用自旋锁加锁,就可以同时多线(进)程对此结构体进行操作,主要是保护ready_list*/
/*
* This mutex is used to ensure that files are not removed
* while epoll is using them. This is held during the event
* collection loop, the file cleanup path, the epoll file exit
* code and the ctl operations.
*/
struct mutex mtx; /*防止使用时被删除*/
/* Wait queue used by sys_epoll_wait() */
wait_queue_head_t wq; /*sys_epoll_wait()使用的等待队列*/
/* Wait queue used by file->poll() */
wait_queue_head_t poll_wait; /*file->epoll()使用的等待队列*/
/* List of ready file descriptors */
struct list_head rdllist; /*事件就绪链表*/
/* RB tree root used to store monitored fd structs */
struct rb_root rbr; /*用于管理当前epoll关注的文件描述符(树根)*/
/*
* This is a single linked list that chains all the "struct epitem" that
* happened while transfering ready events to userspace w/out
* holding ->lock.
*/
struct epitem *ovflist; /*在向用户空间传输就绪事件的时候,将同时发生事件的文件描述符链入到这个链表里面*/
}; |
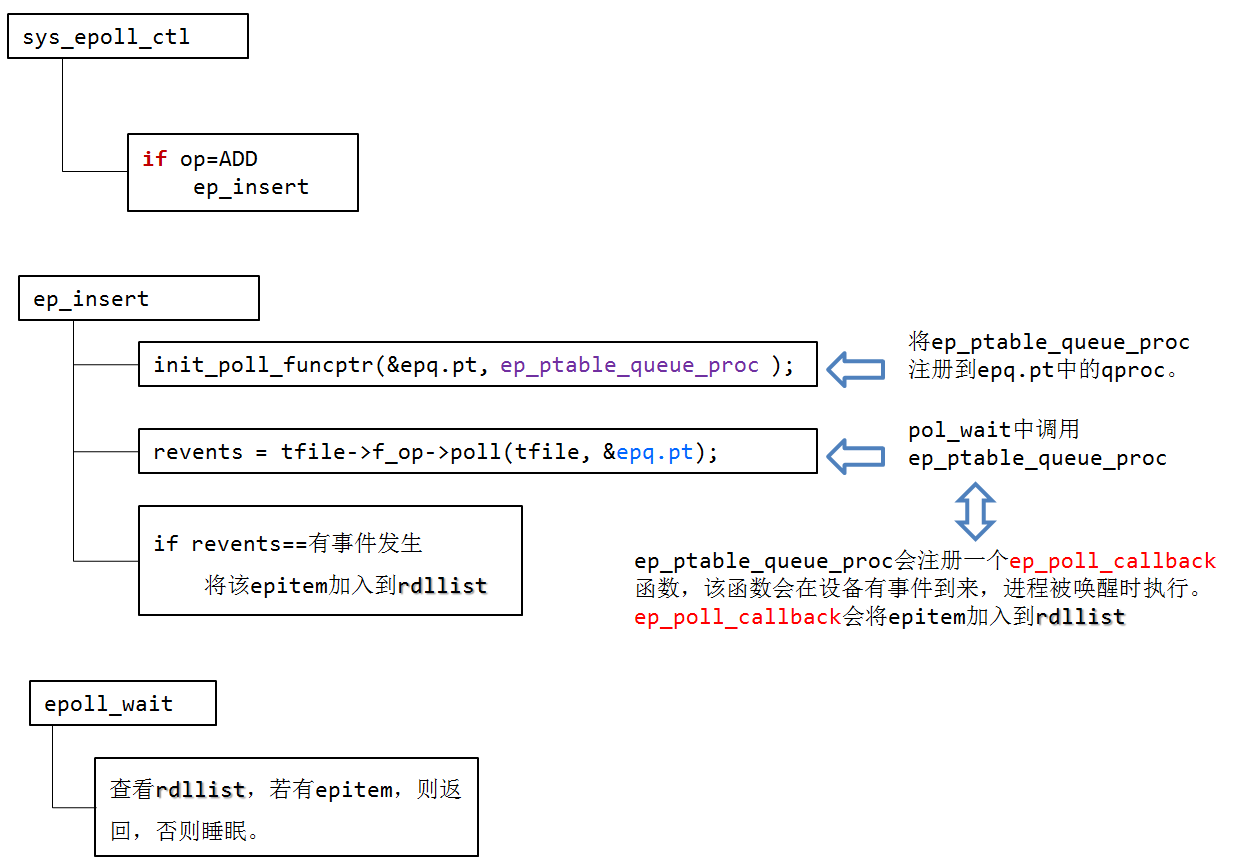
函数调用关系
epoll_create
每个eventpoll通过epoll_create()创建:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
asmlinkage long sys_epoll_create(int size)
{
int error, fd = -1;
struct eventpoll *ep;
DNPRINTK(3, (KERN_INFO "[%p] eventpoll: sys_epoll_create(%d)\n",
current, size));
/*
* Sanity check on the size parameter, and create the internal data
* structure ( "struct eventpoll" ).
*/
error = -EINVAL;
/*为ep分配内存并进行初始化*/
if (size <= 0 || (error = ep_alloc(&ep)) < 0) {
fd = error;
goto error_return;
}
/*
* Creates all the items needed to setup an eventpoll file. That is,
* a file structure and a free file descriptor.
*/
/*调用anon_inode_getfd新建一个struct file,也就是epoll可以看成一个文件(由* 于没有任何文件系统,为匿名文件)。并且将主结构体struct eventpoll *ep放入* file->private项中进行保存(sys_epoll_ctl会取用)*/
fd = anon_inode_getfd("[eventpoll]", &eventpoll_fops, ep);
if (fd < 0)
ep_free(ep);
error_return:
DNPRINTK(3, (KERN_INFO "[%p] eventpoll: sys_epoll_create(%d) = %d\n",
current, size, fd));
return fd;
}
|
epoll_ctl
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
|
asmlinkage long sys_epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd,
struct epoll_event __user *event)
{
int error;
struct file *file, *tfile;
struct eventpoll *ep;
struct epitem *epi;
struct epoll_event epds;
DNPRINTK(3, (KERN_INFO "[%p] eventpoll: sys_epoll_ctl(%d, %d, %d, %p)\n",
current, epfd, op, fd, event));
error = -EFAULT;
/*判断参数合法性,将__user *event 复制给epds*/
if (ep_op_has_event(op) &&
copy_from_user(&epds, event, sizeof(struct epoll_event)))
goto error_return;
/* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */
error = -EBADF;
file = fget(epfd); /*epoll fd对应的文件对象*/
if (!file)
goto error_return;
/* Get the "struct file *" for the target file */
tfile = fget(fd); /*fd对应的文件对象*/
if (!tfile)
goto error_fput;
/* The target file descriptor must support poll */
error = -EPERM;
if (!tfile->f_op || !tfile->f_op->poll)
goto error_tgt_fput;
...
/*
* At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains
* our own data structure.
*/
ep = file->private_data; /*在create时存入进去的(anon_inode_getfd),现在取用。*/
mutex_lock(&ep->mtx);
/*
* Try to lookup the file inside our RB tree, Since we grabbed "mtx"
* above, we can be sure to be able to use the item looked up by
* ep_find() till we release the mutex.
*/
epi = ep_find(ep, tfile, fd); /*防止重复添加(在ep的红黑树中查找是否已经存在这个fd)*/
switch (op) {
case EPOLL_CTL_ADD: /*新增一个监听fd*/
if (!epi) {
epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP; /*默认包含POLLERR和POLLHUP事件*/
error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tfile, fd); /*在ep的红黑树中插入这个fd对应的epitm结构体。*/
} else /*重复添加(在ep的红黑树中查找已经存在这个fd)。*/
error = -EEXIST;
break;
...
}
...
return error;
}
其中ep_insert的实现如下:
```c
static int ep_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event *event,
struct file *tfile, int fd)
{
int error, revents, pwake = 0;
unsigned long flags;
struct epitem *epi;
struct ep_pqueue epq;
error = -ENOMEM;
/*分配一个epitem结构体来保存每个存入的fd*/
if (!(epi = kmem_cache_alloc(epi_cache, GFP_KERNEL)))
goto error_return;
/* Item initialization follow here ... */
/*初始化该结构体*/
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->rdllink);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->fllink);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->pwqlist);
epi->ep = ep;
ep_set_ffd(&epi->ffd, tfile, fd);
epi->event = *event;
epi->nwait = 0;
epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
/* Initialize the poll table using the queue callback */
epq.epi = epi;
/*安装poll回调函数*/
init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);
/*
* Attach the item to the poll hooks and get current event bits.
* We can safely use the file* here because its usage count has
* been increased by the caller of this function. Note that after
* this operation completes, the poll callback can start hitting
* the new item.
*/
/*
* 调用poll函数来获取当前事件位,其实是利用它来调用注册函数ep_ptable_queue_proc(poll_wait中调用)。
* 如果fd是套接字,f_op为socket_file_ops,poll函数是sock_poll()。
* 如果是TCP套接字的话,进而会调用到tcp_poll()函数。此处调用poll函数查看当前文件描述符的状态,存储在revents中。
* 在poll的处理函数(tcp_poll())中,会调用sock_poll_wait(),
* 在sock_poll_wait()中会调用到epq.pt.qproc指向的函数,也就是ep_ptable_queue_proc()。
*/
revents = tfile->f_op->poll(tfile, &epq.pt);
/* Add the current item to the list of active epoll hook for this file */
spin_lock(&tfile->f_ep_lock);
list_add_tail(&epi->fllink, &tfile->f_ep_links);
spin_unlock(&tfile->f_ep_lock);
/*
* Add the current item to the RB tree. All RB tree operations are
* protected by "mtx", and ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held.
*/
ep_rbtree_insert(ep, epi); /*将该epi插入到ep的红黑树中*/
/* We have to drop the new item inside our item list to keep track of it */
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
/* If the file is already "ready" we drop it inside the ready list */
/*
* revents & event->events:刚才fop->poll的返回值中标识的事件有用户event关心的事件发生。
* !ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink):epi的ready队列中有数据。ep_is_linked用于判断队列是否为空。
*/
/* 如果要监视的文件状态已经就绪并且还没有加入到就绪队列中,则将当前的epitem加入到就绪队列中.如果有进程正在等待该文件的状态就绪,则唤醒一个等待的进程。 */
if ((revents & event->events) && !ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {
/*将当前epi插入到ep->ready队列中。*/
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
/* Notify waiting tasks that events are available */
/* 如果有进程正在等待文件的状态就绪,也就是调用epoll_wait睡眠的进程正在等待,则唤醒一个等待进程。waitqueue_active(q) 等待队列q中有等待的进程返回1,否则返回0。*/
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
/* 如果有进程等待eventpoll文件本身(???)的事件就绪,则增加临时变量pwake的值,pwake的值不为0时,在释放lock后,会唤醒等待进程。 */
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/* We have to call this outside the lock */
if (pwake)
/*唤醒等待eventpoll文件状态就绪的进程*/
ep_poll_safewake(&psw, &ep->poll_wait);
DNPRINTK(3, (KERN_INFO "[%p] eventpoll: ep_insert(%p, %p, %d)\n",
current, ep, tfile, fd));
return 0;
...
}
|
init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);和revents = tfile->f_op->poll(tfile, &epq.pt);这两个函数将ep_ptable_queue_proc注册到epq.pt中的qproc。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
typedef struct poll_table_struct {
poll_queue_proc qproc;
unsigned long key;
}poll_table;
|
执行f_op->poll(tfile, &epq.pt)时,XXX_poll(tfile, &epq.pt)函数会执行poll_wait(),poll_wait()会调用epq.pt.qproc函数,即ep_ptable_queue_proc。
ep_ptable_queue_proc函数如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
/*当poll醒来时就回调用该函数,在文件操作中的poll函数中调用,将epoll的回调函数加入到目标文件的唤醒队列中。如果监视的文件是套接字,参数whead则是sock结构的sk_sleep成员的地址*/
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead,
poll_table *pt)
{
/*pt获取struct ep_queue的epi字段。*/
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_epqueue(pt);
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
if (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL))) {
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
pwq->whead = whead;
pwq->base = epi;
add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
list_add_tail(&pwq->llink, &epi->pwqlist);
epi->nwait++;
} else {
/* We have to signal that an error occurred */
/*如果分配内存失败,则将nwait置为-1,表示发生错误,即内存分配失败,或者已发生错误*/
epi->nwait = -1;
}
}
|
其中struct eppoll_entry定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
struct eppoll_entry {
struct list_head llink;
struct epitem *base;
wait_queue_t wait;
wait_queue_head_t *whead;
};
|
ep_ptable_queue_proc 函数完成 epitem 加入到特定文件的wait队列任务。
ep_ptable_queue_proc有三个参数:
1
2
3
4
5
|
struct file *file; 该fd对应的文件对象
wait_queue_head_t *whead; 该fd对应的设备等待队列(同select中的mydev->wait_address)
poll_table *pt; f_op->poll(tfile, &epq.pt)中的epq.pt
|
在ep_ptable_queue_proc函数中,引入了另外一个非常重要的数据结构eppoll_entry。eppoll_entry主要完成epitem和epitem事件发生时的callback(ep_poll_callback)函数之间的关联。首先将eppoll_entry的whead指向fd的设备等待队列(同select中的wait_address),然后初始化eppoll_entry的base变量指向epitem,最后通过add_wait_queue将epoll_entry挂载到fd的设备等待队列上。完成这个动作后,epoll_entry已经被挂载到fd的设备等待队列。
由于ep_ptable_queue_proc函数设置了等待队列的ep_poll_callback回调函数。所以在设备硬件数据到来时,硬件中断处理函数中会唤醒该等待队列上等待的进程时,会调用唤醒函数ep_poll_callback
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
static int ep_poll_callback(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key)
{
int pwake = 0;
unsigned long flags;
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_wait(wait);
struct eventpoll *ep = epi->ep;
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
/*
* If the event mask does not contain any poll(2) event, we consider the
* descriptor to be disabled. This condition is likely the effect of the
* EPOLLONESHOT bit that disables the descriptor when an event is received,
* until the next EPOLL_CTL_MOD will be issued.
*/
if (!(epi->event.events & ~EP_PRIVATE_BITS))
goto out_unlock;
...
/* If this file is already in the ready list we exit soon */
if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink))
goto is_linked;
/*将该fd加入到epoll监听的就绪链表中*/
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
is_linked:
/*
* Wake up ( if active ) both the eventpoll wait list and the ->poll()
* wait list.
*/
/*唤醒调用epoll_wait()函数时睡眠的进程。用户层epoll_wait(...) 超时前返回。*/
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
out_unlock:
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/* We have to call this outside the lock */
if (pwake)
ep_poll_safewake(&psw, &ep->poll_wait);
return 1;
}
|
所以ep_poll_callback函数主要的功能是将被监视文件的等待事件就绪时,将文件对应的epitem实例添加到就绪队列中,当用户调用epoll_wait()时,内核会将就绪队列中的事件报告给用户。
epoll_wait
epoll_wait实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
asmlinkage long sys_epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, int timeout)
{
int error;
struct file *file;
struct eventpoll *ep;
/* The maximum number of event must be greater than zero */
if (maxevents <= 0 || maxevents > EP_MAX_EVENTS)
return -EINVAL;
/* Verify that the area passed by the user is writeable */
/* 检查用户空间传入的events指向的内存是否可写。参见__range_not_ok()。*/
if (!access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, events, maxevents * sizeof(struct epoll_event))) {
error = -EFAULT;
goto error_return;
}
/* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */
/* 获取epfd对应的eventpoll文件的file实例,file结构是在epoll_create中创建。 */
error = -EBADF;
file = fget(epfd);
if (!file)
goto error_return;
/*
* We have to check that the file structure underneath the fd
* the user passed to us _is_ an eventpoll file.
*/
/* 通过检查epfd对应的文件操作是不是eventpoll_fops 来判断epfd是否是一个eventpoll文件。如果不是则返回EINVAL错误。 */
error = -EINVAL;
if (!is_file_epoll(file))
goto error_fput;
/*
* At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains
* our own data structure.
*/
ep = file->private_data;
/* Time to fish for events ... */
error = ep_poll(ep, events, maxevents, timeout);
error_fput:
fput(file);
error_return:
return error;
}
|
ep_poll
epoll_wait调用ep_poll,ep_poll实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
|
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, long timeout)
{
int res, eavail;
unsigned long flags;
long jtimeout;
wait_queue_t wait;
/*
* Calculate the timeout by checking for the "infinite" value ( -1 )
* and the overflow condition. The passed timeout is in milliseconds,
* that why (t * HZ) / 1000.
*/
/* timeout是以毫秒为单位,这里是要转换为jiffies时间。这里加上999(即1000-1),是为了向上取整。 */
jtimeout = (timeout < 0 || timeout >= EP_MAX_MSTIMEO) ?
MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT : (timeout * HZ + 999) / 1000;
retry:
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
res = 0;
if (list_empty(&ep->rdllist)) {
/*
* We don't have any available event to return to the caller.
* We need to sleep here, and we will be wake up by
* ep_poll_callback() when events will become available.
*/
/* 没有事件,所以需要睡眠。当有事件到来时,睡眠会被ep_poll_callback函数唤醒。*/
init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current); /*将current进程放在wait这个等待队列中。*/
wait.flags |= WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE;
/* 将当前进程加入到eventpoll的等待队列中,等待文件状态就绪或直到超时,或被信号中断。 */
__add_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
for (;;) {
/*
* We don't want to sleep if the ep_poll_callback() sends us
* a wakeup in between. That's why we set the task state
* to TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE before doing the checks.
*/
/* 执行ep_poll_callback()唤醒时应当需要将当前进程唤醒,所以当前进程状态应该为“可唤醒”TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE */
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
/* 如果就绪队列不为空,也就是说已经有文件的状态就绪或者超时,则退出循环。*/
if (!list_empty(&ep->rdllist) || !jtimeout)
break;
/* 如果当前进程接收到信号,则退出循环,返回EINTR错误 */
if (signal_pending(current)) {
res = -EINTR;
break;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/*
* 主动让出处理器,等待ep_poll_callback()将当前进程唤醒或者超时,返回值是剩余的时间。
* 从这里开始当前进程会进入睡眠状态,直到某些文件的状态就绪或者超时。
* 当文件状态就绪时,eventpoll的回调函数ep_poll_callback()会唤醒在ep->wq指向的等待队列中的进程。
*/
jtimeout = schedule_timeout(jtimeout);
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
}
__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
}
/* Is it worth to try to dig for events ? */
/*
* ep->ovflist链表存储的向用户传递事件时暂存就绪的文件。
* 所以不管是就绪队列ep->rdllist不为空,或者ep->ovflist不等于
* EP_UNACTIVE_PTR,都有可能现在已经有文件的状态就绪。
* ep->ovflist不等于EP_UNACTIVE_PTR有两种情况,一种是NULL,此时
* 可能正在向用户传递事件,不一定就有文件状态就绪,
* 一种情况时不为NULL,此时可以肯定有文件状态就绪,
* 参见ep_send_events()。
*/
eavail = !list_empty(&ep->rdllist);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/*
* Try to transfer events to user space. In case we get 0 events and
* there's still timeout left over, we go trying again in search of
* more luck.
*/
/* 如果没有被信号中断,并且有事件就绪,但是没有获取到事件(有可能被其他进程获取到了),并且没有超时,则跳转到retry标签处,重新等待文件状态就绪。 */
if (!res && eavail &&
!(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)) && jtimeout)
goto retry;
/* 返回获取到的事件的个数或者错误码 */
return res;
}
|
ep_send_events()函数向用户空间发送就绪事件。
ep_send_events()函数将用户传入的内存简单封装到ep_send_events_data结构中,然后调用ep_scan_ready_list()将就绪队列中的事件传入用户空间的内存。
用户空间访问这个结果,进行处理。